Molecular mechanisms of innate immunity
Molecular simulations of immune re3ceptors to understand and treat autoimmune disease
Student intake
This project is open for Honours, Master and PhD students.
Research theme
Research themes
Project status
Project status
Current
Content navigation
About
Image
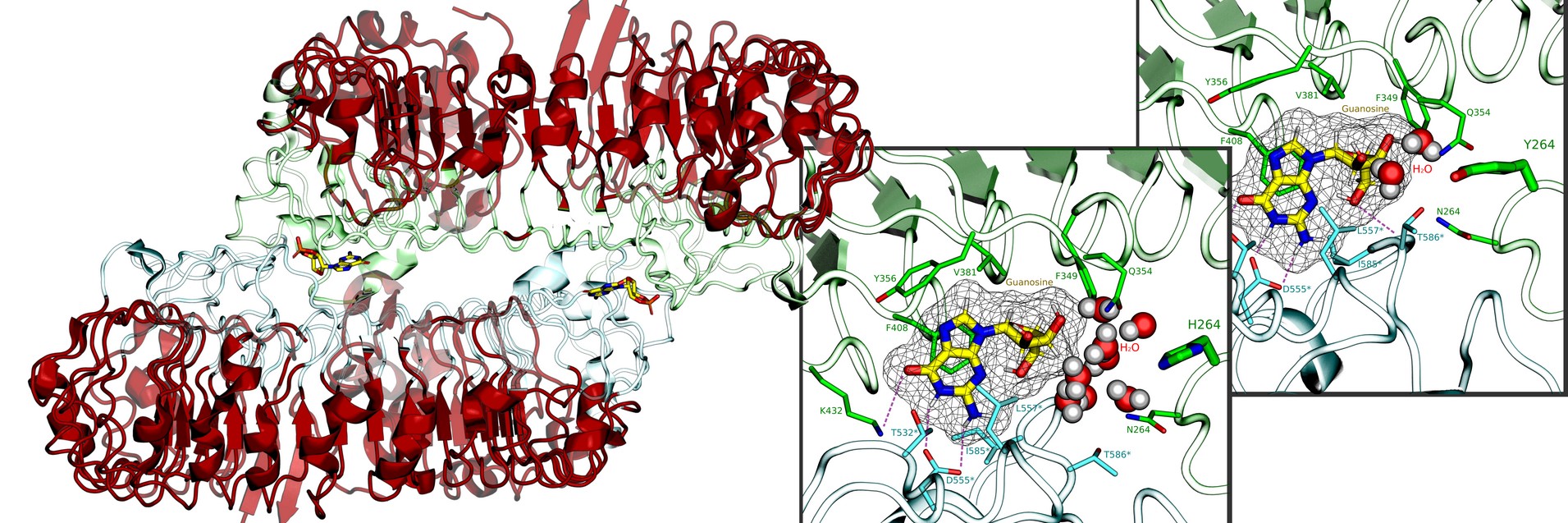
Invading pathogens like viruses are detected by the innate immune system when fragments of their DNA or RNA bind to recognition toll-like receptors. Mutations in these receptors that either lead to either overactive or underactive immune systems can be responsible for debilitating autoimmune diseases or severe COVID-19 and other viral disease. We aim to undersatnd how this recognition occurs, how pathogens are distinguished from endogenous genetic material and how these receptors can be targetted to treat autoimmune disease.

