Past events
This page lists RSB past events.
Nutritional deficiencies are a leading cause of human susceptibility to infectious diseases and antibiotic treatment failure. Specifically, our intake of dietary lipids has changed dramatically, yet microbe-lipid interactions during infection are poorly understood.
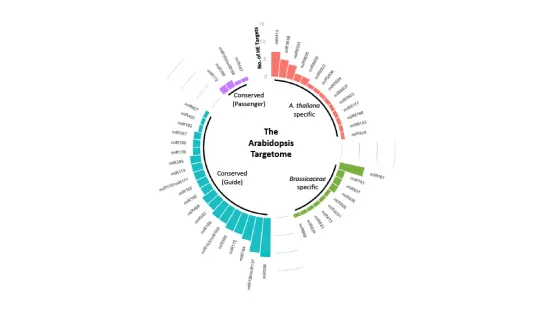
In plants, microRNAs (miRNAs) are short non-coding RNAs of approximately 20-24 nt in length which are involved in post-transcriptional regulation of genes controlling many fundamental biological pathways.

Specialised metabolites are one of the major means of how microbes and sessile organisms express extended phenotype for the selective advantage of the organisms —or, more fundamentally, their genes.
Bacterial infections remain a global public health challenge and there is a critical need for the identification and molecular understanding of new targets for antimicrobial design.

Natural capital describes the stocks of renewable and non-renewable resources (e.g. plants, animals, air, water, soils and minerals) that produce flows of benefits to people.
Source-to-sink allocation of, and sink-to-sink competition for, photoassimilates, mainly in the form of sucrose, play a key role in determining energy and resource distribution in plants for growth and reproduction.
Current treatments for malaria are threatened by drug resistance, and new antimalarials are urgently required to ensure the continued ability to treat malaria infections into the future.

B0AT1 (Slc6a19) is a sodium-dependent neutral amino acid transporter catalyzing the secondary active transport of neutral amino acids across the brush border membrane of the kidney and intestine.

