PS Seminar Series- PhD Exit seminar - An evolutionary and biochemical approach to gain insight into SAL1-PAP retrograde signalling
Plant acclimation to environmental stress involves complex cellular processes including chloroplast-to-nucleus communication mediated by signals such as 3’-phosphoadenosine 5’-phosphate (PAP) and its catabolic phosphatase, SAL1.
Speakers
Event series
Content navigation
Description
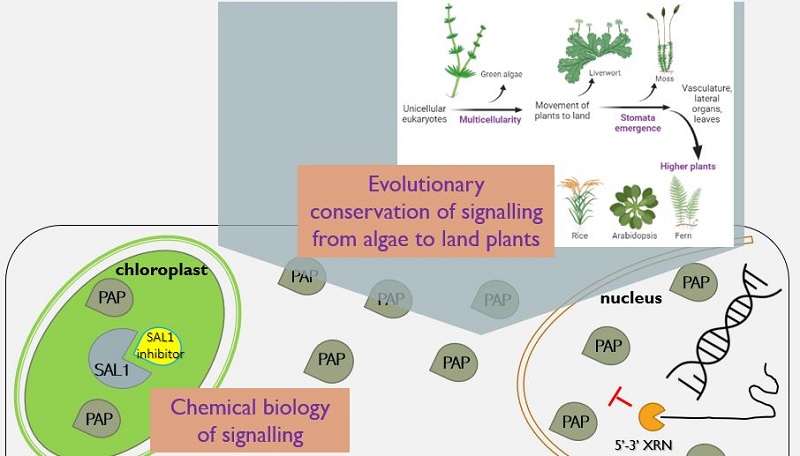
Abstract - Plant acclimation to environmental stress involves complex cellular processes including chloroplast-to-nucleus communication mediated by signals such as 3’-phosphoadenosine 5’-phosphate (PAP) and its catabolic phosphatase, SAL1. Cellular levels of PAP are regulated by SAL1, and PAP interacts with nuclear 5’-3’ exoribonucleases (XRNs) to influence RNA metabolism, thereby up-regulating stress-responsive genes.
To date, studies on the SAL1-PAP-XRN pathway have been mostly limited to Arabidopsis thaliana, a dicot angiosperm, yet the SAL1 enzyme is conserved in all plant species including aquatic algae and early land plants which grow in vastly different habitats to angiosperms. Therefore, the first aim of my PhD was to investigate the evolutionary conservation of SAL1-PAP signalling in early land plant species. I generated CRISPR sal1 knockouts in Marchantia polymorpha, which showed similar phenotypes to Arabidopsis sal1 such as growth defects and higher stress tolerance. RNA sequencing analysis revealed that 17% of the differentially regulated genes in Marchantia sal1 are high-light responsive, with genes under the same biological processes being differentially regulated in the Marchantia and Arabidopsis sal1 mutants. These results suggest that chloroplast stress-signalling pathways such as SAL1-PAP arose early, and have been conserved, in land plant evolution.
The growth defects of sal1 mutants illustrate the need for more refined approaches to manipulate SAL1 activity, such that the “true” cellular stress response to PAP signalling can be disentangled from downstream pleiotropic effects. The second aim of my PhD was to develop novel chemical tools that modulate SAL1 activity to elicit PAP accumulation to high levels. I identified small molecule SAL1 inhibitors, which were optimised for highest inhibitory potency towards SAL1 through chemical analoguing. Mutagenesis of the SAL1 protein and molecular dynamic simulations revealed potential binding sites and mechanisms of action for these inhibitors. Preliminary assays show that some of these inhibitors can enhance stress tolerance when applied to leaves. Consequently, these inhibitors may be utilised to fine tune PAP signalling to better understand its role in cellular signalling, and potentially as agrochemicals to enhance crop stress tolerance in the long-term.
Taken together, the results from my project provide an evolutionary context to chloroplast signalling mediated by SAL1-PAP, and initiated steps towards the development of an agrochemical tool for rapid accumulation of PAP to be utilised in future studies.
Biography - I completed my Bachelor of Medical Sciences (Honours) at ANU in 2014, working on characterising novel candidate genes involved in carotenoid biosynthesis. After Honours, I worked as a research assistant in John Curtin School of Medical Research in Burgio lab, developing CRISPR tools in mammalian system, from 2015-2018. Then, I pursued my PhD in 2018 in the Pogson lab at ANU.
Location
Slatyer Seminar Room, N2011, Level 2, RN Robertson Building (46)




